Passive House & LEED: Why compromise when you can have the best of both worlds?
2020.10.20

If your company is planning a LEED building or renovation project, learn how incorporating Passive House design can help you maximize sustainability, energy efficiency and worker comfort.
The two systems both aim to create Green Buildings which are better for the environment and the people that occupy them, but they go about it in different ways. By meeting the requirements of both systems, you can ensure that your building is truly efficient and delivering the energy savings promised.
So what are the two systems and their respective benefits and limitations?
What is LEED?
- • According to the US Green Building Council, LEED is a rating system that promotes “healthy, highly efficient, and cost-saving green buildings.”
- • Certification is based on Points which can be collected across eight different categories, including Materials & Resources, Indoor Environmental Quality, and Water Efficiency and will result in rating levels from Certified up to Platinum.
What are the Benefits of LEED?
- • The goal of LEED is to promote a holistic approach to the design and construction of buildings which encourages evaluation of impacts and benefits to the environment and human health.
- • In theory, a LEED certified building should have a smaller environmental footprint, generate less waste during construction, use less energy and provide occupants with a better indoor environment than a conventional building on the same site.
What are the limitations of LEED?
- • Since LEED tries to look at many aspects of design and performance simultaneously and allows shifting of points between categories, it frequently results in buildings which are not significantly more efficient than conventional designs.
- • The USGBC admits that "current information indicates that most buildings do not perform as well as design metrics indicate. As a result, building owners might not obtain the benefits promised."
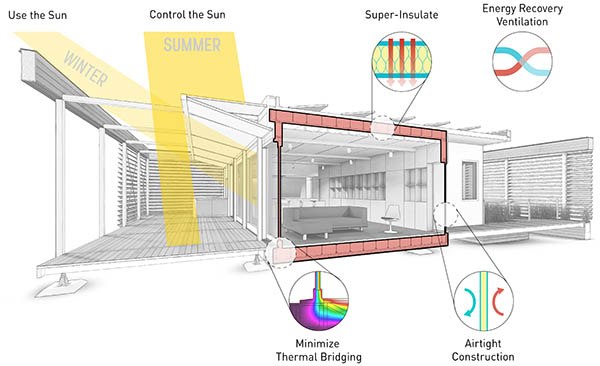
What is Passive House?
- • Passive House is a set of design standards that strictly limit the amount of energy a building can use based on its size, while ensuring high levels of ventilation and fresh air.
- • Certification is based on rigorous modelling, evaluation and performance testing of airtightness, ventilation, thermal bridging and electrical loads. Higher levels of certification are achievable by adding renewable energy generation through solar or wind.
What are the Benefits of Passive House?
- • Passive House design requires the creation of a detailed energy model that accurately determines the energy usage and operating costs of the final building.
- • The end result is a high performance building that requires only a very small quantifiable amount of energy for heating or cooling and provides great indoor air quality.
What are the limitations of Passive House?
- • Passive House is laser focused on energy use and comfort and doesn’t attempt to address broader issues of siting, material sourcing, water use or construction processes.
So how can I get the benefits of both systems?
Happily, the two systems are complementary, and meeting the two standards is easy if the goals are determined early in the design process.
Passive House is more rigorous in terms of energy use and performance, while LEED requires additional planning and documentation to meet its requirements for site, materials, water and construction processes.
Incorporating LEED and Passive House standards will ensure that your building is built to the highest standards of efficiency while guaranteeing occupant comfort and the smallest possible environmental footprint.


